Healthcare workers play a crucial role in our society, providing care and support to those in need. However, their profession often comes with physical and emotional challenges that can lead to injuries and burnout.
While healthcare workers are often celebrated for their dedication and compassion, it’s important to acknowledge the toll their work can take on their bodies and minds. Long hours, physically demanding tasks, and emotional stressors can lead to a range of injuries and health issues.
In this article, we’ll explore the most common injuries that healthcare workers face.
Understanding the Risk Factors
Long Hours and Stress
Healthcare professionals frequently work extended shifts, often under high-pressure conditions. This combination of long hours and emotional stress can lead to physical and mental fatigue, increasing the risk of injuries and burnout. Recognizing the signs of stress and implementing strategies to manage it is crucial for healthcare workers’ well-being.
Patient Handling
Patient handling is a fundamental aspect of healthcare, but it can also be a significant source of injuries. Lifting and transferring patients can strain the back and musculoskeletal system, leading to injuries.
Repetitive Tasks
Repetitive tasks, such as charting and documentation, are inherent to healthcare work. However, the constant repetition of motions can result in conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome and other repetitive strain injuries.
Common Injuries in Healthcare Workers
Musculoskeletal Injuries
Back Strains and Injuries
Healthcare workers are no strangers to the physical demands of their profession, often required to lift and move patients or heavy medical equipment. As a result, back strains and injuries are among the most common musculoskeletal problems faced by healthcare professionals. These injuries can manifest as acute pain, chronic discomfort, or even debilitating conditions. To address this issue, it’s crucial for healthcare workers to learn proper lifting techniques, utilize assistive devices when available, and engage in regular back-strengthening exercises. Additionally, maintaining a healthy work-life balance and seeking prompt medical attention for any signs of back trouble are vital steps toward preventing and recovering from these injuries.
Sprains and Strains
The nature of healthcare work often involves quick and repetitive movements, which can lead to sprains and strains in various parts of the body, such as the wrists, shoulders, and knees. These injuries can result from tasks like turning patients, adjusting medical equipment, or even simply standing for extended periods. To reduce the risk of sprains and strains, healthcare workers should be aware of their body mechanics, practice good ergonomics, and take regular breaks to stretch and rest. Adequate warm-up exercises before shifts can also help prepare the body for the physical demands of the job.
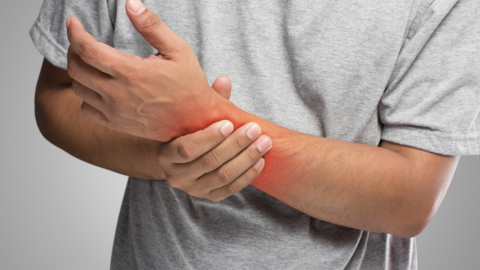
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Healthcare professionals who spend substantial time typing or documenting patient information on computers are susceptible to developing carpal tunnel syndrome. This condition occurs when pressure is placed on the median nerve in the wrist, leading to symptoms like numbness, tingling, and pain in the hand and fingers. To mitigate the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome, ergonomic workstation setups are essential. This includes using an ergonomic keyboard and mouse, maintaining proper wrist positioning, and taking frequent breaks to stretch and flex the wrists. Early recognition of symptoms is crucial, as prompt intervention and lifestyle adjustments can prevent the condition from progressing.
Mental Health Challenges
Burnout
Burnout is a pervasive issue in the healthcare industry, primarily stemming from the emotional and mental toll of caring for patients, especially during demanding and prolonged shifts. Healthcare workers experiencing burnout may find themselves emotionally exhausted, detached from their work, and experiencing a reduced sense of accomplishment. It’s essential to recognize the signs of burnout, such as increased irritability, fatigue, and diminished enthusiasm for the job. To combat burnout, healthcare professionals should prioritize self-care, seek support from colleagues and mental health professionals, and establish a healthy work-life balance. Institutions can also contribute by implementing programs that address staff well-being and provide resources for managing stress.
Compassion Fatigue
Compassion fatigue, often referred to as secondary traumatic stress, is a phenomenon where healthcare workers become emotionally drained and overwhelmed due to their exposure to patients’ suffering and trauma. It can lead to feelings of sadness, guilt, and even a sense of hopelessness. Healthcare organizations should prioritize strategies to prevent and address compassion fatigue, such as offering regular debriefing sessions and psychological support. Additionally, self-awareness is key for healthcare workers to recognize when they are experiencing compassion fatigue and take appropriate steps to seek help and engage in self-care activities to recharge emotionally.
Conclusion
In conclusion, healthcare workers are the backbone of our society, tirelessly providing care and support to those in need. Their dedication and compassion are unwavering, but it’s crucial to recognize the physical and emotional toll their profession can take. This article has shed light on the most common injuries and challenges faced by healthcare workers and provided insights into how to prevent and mitigate these issues.
From musculoskeletal injuries like back strains and carpal tunnel syndrome to the mental health challenges of burnout and compassion fatigue, healthcare professionals face unique and demanding work conditions. Understanding the risk factors associated with long hours, patient handling, and repetitive tasks is the first step toward safeguarding their well-being.
Contact WorkSafe to find out how we can help your company today!
Working to keep you safe, healthy, and productive,

